I’m about to share Half 2 of the letter, the place I’ll take you deep into the “inside baseball” of our funding course of. Particularly, I’ll talk about how we construction and decide the place measurement of every inventory in our portfolios – one thing I haven’t lined earlier than (not less than not on this element) and haven’t seen different buyers talk about a lot both.
If you happen to learn my articles primarily for the tales, be happy to skip this one. However in the event you’re a critical weekend warrior investor, don’t skim – learn this fastidiously. This portfolio building framework is essential, as a result of it skews the portfolio towards larger returns per unit of danger, the place danger means everlasting lack of capital. Whereas this is only one module of our funding course of, it’s an exceptionally necessary one.
Inside Baseball: How We Construct Portfolios
An funding course of is a residing organism as a result of it’s utilized by residing creatures. We proceed to enhance it and have made appreciable strides over time. The largest leap got here in 2016, brought on by a really tough and fairly painful 2015 (I wrote about ache being an amazing instigator within the “Ache, Opera and Investing” chapter of Soul within the Recreation). Then in early 2019, our funding course of took one other important step ahead by assigning scores to our corporations throughout two dimensions:
- High quality: The very best high quality corporations have been graded A, the bottom D
- Valuation: The most cost effective corporations have been assigned a 1, the most costly a 4
This will likely not appear to be a lot, nevertheless it helped us quantify our in any other case very qualitative analysis and considerably enhance our portfolio building.
Reasonably than resting on our laurels after our latest success, I wished to capitalize on what we had realized and enhance what we do. In reviewing our positions over time, I found a bias – I didn’t like giving C and D grades. I noticed that the scars from a decade of attending college in Russia and receiving poor grades have been stronger than my rational evaluation of those corporations. (Aspect be aware: I used to show investing on the College of Denver however give up as a result of I hated giving out unhealthy grades.)
On the one hand, this may not look like an enormous deal; in any case, we solely wished to personal A and B corporations. However the authentic intent of this method was to take the best high quality layer of the worldwide inventory market and phase it into 4 helpful classes. My aversion to C and D grades flattened the nuanced qualitative understanding we had developed about these corporations. We would have liked a brand new ranking system that captured these distinctions.
And so we’ve modified our scores to A, B, B-, and V. Right here’s what these grades imply:
- A: An organization with an unassailable moat, unbelievable administration, flawless steadiness sheet, excessive return on capital, excessive recurrence of revenues, and a non-cyclical enterprise.
- B: An organization with most of the traits of an A, however which has a sure flaw. Perhaps its income recurrence could also be decrease, or we don’t have sufficient knowledge to totally consider administration. To be clear, the administration isn’t “unhealthy” – if it have been unhealthy, we merely wouldn’t purchase it. There’s just a few issue about it that makes the corporate decrease in high quality than these we give an A to.
- B-: Might be an A or B firm in a cyclical, commodity enterprise, situated in a riskier nation (for instance someplace in Latin America). Or could possibly be an A or B non-cyclical firm within the early section of a turnaround. In both case, these corporations face transitional “headwinds” that high quality corporations can work by means of, making it decrease in high quality than B corporations.
- V: A, B, B- corporations are stable compounders which might be aimed toward rising whereas preserving capital. However sure public corporations are early of their company journey and provide substantial asymmetry of returns. In the event that they succeed, they might go up as a lot as 5–20x, but when they fail, losses could also be as excessive as 100% (although within the corporations we’ve checked out, they appear nearer to 30–50%).
These “enterprise” corporations are disruptors, sometimes run by founders who’ve pores and skin within the recreation. Most significantly, they’ve a long-term runway for earnings development, with a big market and a big probability of capturing a considerable share of it.
We’re not changing into enterprise capitalists and gained’t have a portfolio of Vs, however we’ve purchased a couple of of those over the previous couple of months – I’ll point out them later within the letter. This shift introduces important asymmetry to our portfolio on the edges. The core of it would proceed to be A/B/B- shares, whereas Vs convey excessive optionality and hopefully returns.
Presently, throughout all shoppers and all methods, we personal 33 shares in our portfolio: 10 A’s, 12 B’s, 8 B-’s, and solely 3 V’s.
As corporations evolve, so do their scores. Ideally, we would like Vs to show into As. That’s the evolution we search for – corporations that mature from disruptive potential into established high quality.
For instance, Microsoft within the early Eighties would have been a startup, run by formidable founders who aimed to place a private laptop on each desk and in each dwelling. It was a daring, contrarian imaginative and prescient on the time, nevertheless it was additionally one among many younger software program corporations chasing a quickly evolving market.
Microsoft graduated to a V ranking within the late Eighties after it gained the DOS wars with IBM and secured its place because the de facto working system supplier. Arguably it grew to become a B- a couple of years later: the upside remained substantial, however questions emerged round potential competitors and the sturdiness of its moat.
By the mid-to-late Nineties, Microsoft had clearly change into B after which an A – it had established an unassailable moat in working techniques and productiveness software program, generated monumental recurring income, and constructed one of many strongest steadiness sheets available in the market.
Our ranking system is a continuum that captures corporations throughout their whole lifecycle as they transfer up the standard spectrum and even down (this occurred to one among our corporations in 2025). As they transfer up, so does our tolerance for rising their place measurement in our portfolio (which I talk about subsequent).
To be clear, C and D corporations haven’t fully disappeared from our course of; we encounter them often throughout analysis, however we simply aren’t curious about them.
What constitutes C or D corporations? Easy: they don’t seem to be high quality. I like Warren Buffett’s definition of high quality: if the inventory market was closed for ten years, would I be snug holding this inventory?
Inventory market liquidity – the flexibility to purchase and promote at any time – typically turns buyers into merchants. Buffett’s high quality framework, nevertheless, places us firmly within the seat of an investor. C and D corporations are those who fall into the “not snug” bucket.
The fantastic thing about our method is that with 10,000 publicly traded corporations globally and maybe solely a thousand or two assembly our high quality standards, we are able to afford to be extraordinarily selective. We don’t have to compromise on high quality when there’s such an abundance of alternatives to select from – we solely want to seek out 25 shares.
The Energy of Combining High quality with Valuation
Up up to now we’ve mentioned firm high quality and ignored valuation – what the enterprise is value and the way a lot we must always pay for it.
Our valuation evaluation entails two extremes: smothering the enterprise in our fashions with a pillow (stress testing for when “life occurs” – i.e., declining margins, slowing income development, worsening unit economics) and, simply as importantly, envisioning its full potential. By this train, we arrive at a spread of values.
The worst-case state of affairs units our flooring. If we predict the corporate is value $50 in a catastrophe and $100 in essentially the most possible state of affairs, we don’t wish to pay way more than $50. That is our margin of security.
Our high quality ranking system turns into extremely highly effective as soon as it’s married with valuation evaluation. We spend a whole lot of hours researching shares to reach at these two inputs (high quality and honest worth). Right here’s how combining these scores works in observe utilizing a grossly simplified instance (I take advantage of considerably oversimplified numbers right here, however they’re directionally much like what we do in your portfolios).
Let’s say we’ve three corporations, all value $100 in 5 years:

(Between you and me, I’m undecided if Macy’s even deserves a B-, however let’s use it for illustrative functions.)
The sample is obvious: the decrease the standard, the larger the low cost we demand. If all three shares traded at $50 in the present day:
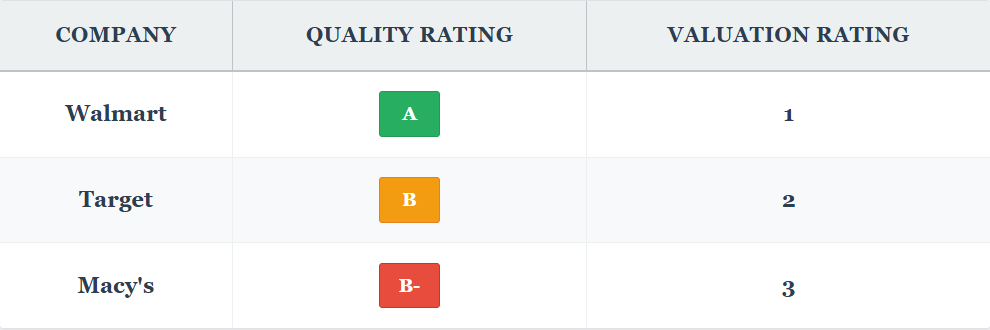
Now, V-rated corporations are a unique animal completely. These are our venture-like investments, and we’re betting on explosive return potential. For these, we measurement positions small (1-3%) and search for multiples of return whereas accepting larger danger of loss.
Place Sizing
The standard ranking and valuation system is a cornerstone of our portfolio building. The upper the standard of the corporate and the extra undervalued it’s, the bigger its place goes to be. This makes excellent sense since larger high quality reduces danger and important undervaluation results in larger returns.
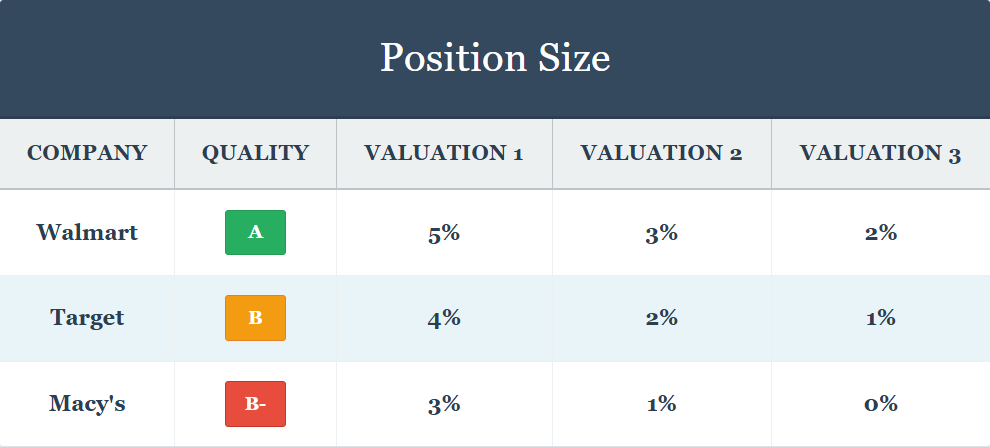
Why is that this necessary? This method forces high-quality corporations which might be considerably undervalued to rise to the highest whereas limiting our publicity to comparatively low-quality corporations. If “life occurs” to a lower-quality firm, the impression on the portfolio is decrease; nevertheless, if issues work out, we’ll get compensated for taking a better danger.
Equality of outcomes was by no means my factor. I like meritocracy, and our portfolio is constructed on advantage.
Generally shoppers ask why we hassle with small place sizes. There are numerous eventualities the place this is smart. For instance, we might have began shopping for a B high quality firm when it had a valuation of 1, then the inventory value went up and it grew to become A3. We should purchase 1% for brand new shoppers.
Moreover, we might have carried out analysis on the corporate and at current consider it deserves a 1% place, however the value might decline or high quality might enhance – in each instances meriting a bigger place measurement. Shopping for even a small place ensures we keep on high of the identify.
Let me finish this primary a part of the letter by sharing three remaining ideas about our valuation course of and place sizing.
First, there’s worth within the course of itself – deciding firm high quality creates inventive friction as we debate whether or not an organization is A or B and problem valuation assumptions. Simply doing this makes us higher buyers and enriches our understanding of what we personal.
Second, quantifying place sizing removes feelings. It’s achieved nearly robotically and calculated every day by our techniques – the variable that adjustments most shouldn’t be high quality or honest worth however market value.
Lastly, as I used to be penning this, I observed a couple of areas the place we are able to already enhance – and that is our aim: to not stand nonetheless, however to repeatedly evolve.
I hope this explains portfolio building, particularly for brand new shoppers.
And yet one more factor – choices
In accounts with enough money and choices buying and selling permissions, we established a number of small choices positions as hedges.
We bought calls on gold (GLD), making a modest guess that gold costs will rise as foreign money debasement continues. We additionally purchased places on 20-year treasuries (TLT) to hedge towards potential spikes in long-term rates of interest ensuing from elevated cash provide. Moreover, we acquired places on the S&P 500 to partially hedge our portfolio towards a broader market decline.
None of those investments function a panacea for present world financial circumstances. The core of our returns and our final success or failure will proceed to rely upon considerate inventory choice.
Key takeaways
- The funding course of developed from painful classes in 2015 and now makes use of a refined ranking system of A, B, B-, and V as an alternative of the unique A-D grades, overcoming psychological biases towards giving poor marks that flattened nuanced firm assessments.
- High quality scores seize your complete company lifecycle: A corporations have unassailable moats and unbelievable administration, B corporations have minor flaws, B- face transitional headwinds, and V corporations are early-stage disruptors with 5-20x upside potential however larger danger.
- Place sizing follows a meritocratic system the place larger high quality corporations with better undervaluation obtain bigger allocations, with A1 corporations getting as much as 7% positions whereas lower-quality names are capped at smaller percentages to restrict draw back publicity.
- The valuation course of entails stress testing companies in catastrophe eventualities and envisioning full potential to determine a spread, demanding larger reductions for lower-quality corporations and utilizing the worst-case state of affairs because the margin of security flooring.
- Portfolio building advantages from quantified inventive friction throughout high quality debates, automated every day place sizing calculations that take away feelings, and selective deal with discovering simply 25 shares from 1000’s of high quality candidates globally, supplemented by small choices hedges on gold, treasuries, and the S&P 500.